combineLatest
RxJava的combineLatest()函数有点像zip()函数的特殊形式。正如我们已经学习的,zip()作用于最近未打包的两个Observables。相反,combineLatest()作用于最近发射的数据项:如果Observable1发射了A并且Observable2发射了B和C,combineLatest()将会分组处理AB和AC,如下图所示:
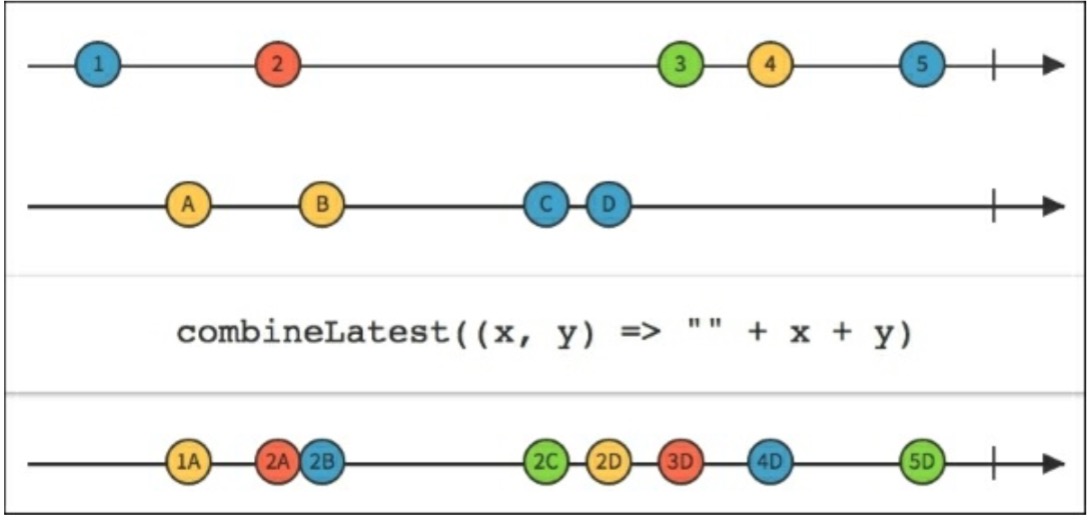
combineLatest()函数接受二到九个Observable作为参数,如果有需要的话或者单个Observables列表作为参数。
从之前的例子中把loadList()函数借用过来,我们可以修改一下来用于combineLatest()实现“真实世界”这个例子:
private void loadList(List<AppInfo> apps) {
mRecyclerView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
Observable<AppInfo> appsSequence = Observable.interval(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.map(position ->apps.get(position.intValue()));
Observable<Long> tictoc = Observable.interval(1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
Observable.combineLatest(appsSequence, tictoc,
this::updateTitle)
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(new Observer<AppInfo>() {
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "Here is the list!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
mSwipeRefreshLayout.setRefreshing(false);
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "Something went wrong!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onNext(AppInfoappInfo) {
if (mSwipeRefreshLayout.isRefreshing()) {
mSwipeRefreshLayout.setRefreshing(false);
}
mAddedApps.add(appInfo);
int position = mAddedApps.size() - 1;
mAdapter.addApplication(position, appInfo);
mRecyclerView.smoothScrollToPosition(position);
}
});
}
这我们使用了两个Observables:一个是每秒钟从我们已安装的应用列表发射一个App数据,第二个是每隔1.5秒发射一个Long型整数。我们将他们结合起来并执行updateTitle()函数,结果如下:
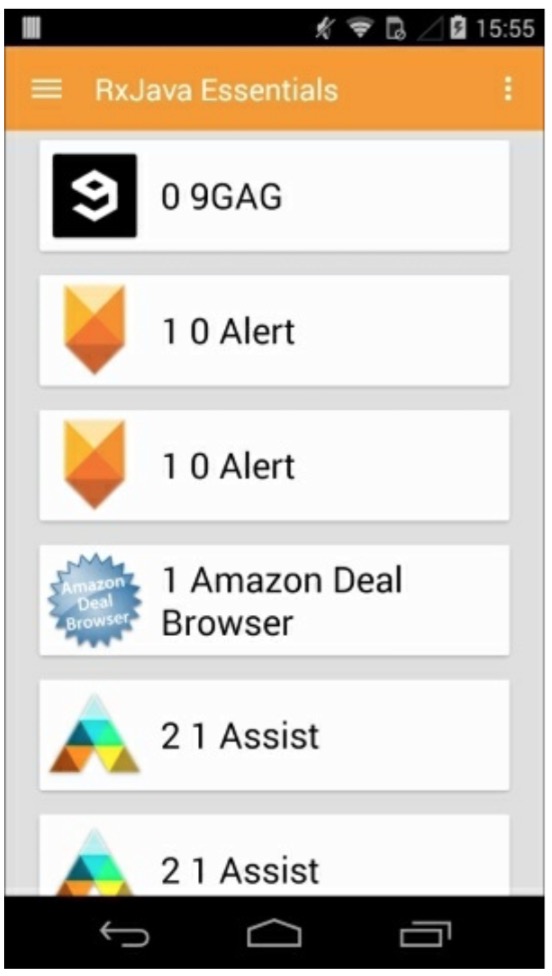
正如你看到的,由于不同的时间间隔,AppInfo对象如我们所预料的那样有时候会重复。